EFEKTIFITAS PENAMBAHAN HEAT SINK ALUMUNIUM PADA PANEL SURYA UNTUK OPTIMALISASI PEMANFAATAN ENERGI TERBARUKAN
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.36499/mim.v21i2.12075Keywords:
Panel Surya, Heat Sink, Pendinginan, Temperatur, EfisiensiAbstract
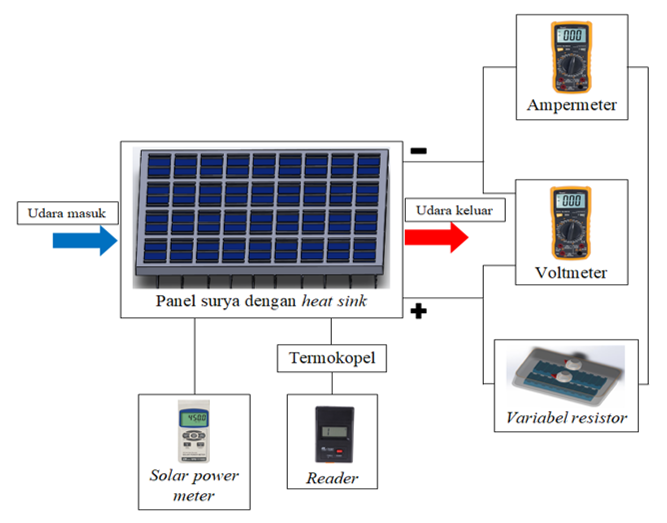
Pada masa sekarang ini panel surya adalah salah satu teknologi yang popular dan terus berkembang dalam aplikasi Energi Baru Terbarukan (EBT). Panel surya berbasis silikon adalah yang paling umum digunakan pada saat ini. Karena Radiasi sinar matahari dapat kita jumpai setiap harinya. Jadi panel surya dapat menjawab terkait permasalahan energi yang ada saat ini. Namun demikian, peningkatan temperatur operasional panel surya dapat menurunkan daya dan efisiensinya. Dan sering kali panel surya akibat tingginya temperature yang ada pada permukaan panel surya sering kali sampai terbakar . Tujuan dari penelitian ini adalah untuk meminimalisir panas yang terjadi pada panel surya akibat dari radiasi yang di tangkap pada permukaan panel surya, sehingga dilakukan penambahan heat sink sebagai media pendingin pada panel surya. diharapkan panel surya akan bekerja optimal terhadap daya dan efisiensi panel surya tersebut tetap terjaga. Metode dari pada penelitian ini yaitu di tempelkanya Heat sink Alumunium pada permukaan bagian bawah panel surya untuk mengurangi panas akibat radiasi yang tinggi. Penelitian yang telah dilakukan dapat disimpulkan mengetahui pengaruh jumlah fin aluminium pada heat sink dengan base Alumunium terdahap unjuk kerja panel surya. Berdasarkan data dan analisa yang telah dilakukan dapat disimpulkan Panel surya dengan heat sink tanpa fin dan 10 fin mampu menurunkan temperatur kerja sebesar 3,3 °C, 6,7 °C lebih rendah dibandingkan panel surya tanpa pendingin dan Panel surya dengan heat sink tanpa fin mampu meningkatkan nilai daya maksimum sebesar 4,58 W dan efisiensi sebesar 1,17% lebih tinggi dibandingkan sel surya tanpa pendingin. Pada panel surya dibandingkan sel surya tanpa pendingin. Sedangkan panel surya dengan heat sink 10 fin mampu meningkatkan nilai daya maksimum sebesar 8,56 W dan efisiensi sebesar 2,23% lebih tinggi dibandingkan sel surya tanpa pendingin.References
Ansari, D., & Jeong, J. H. (2022). A novel variable-height-pinfin isothermal heat sink for densely-packed concentrated photovoltaic systems. Energy Conversion and Management, 258(December 2021), 115519. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2022.115519
Dan, P., & Pendingin, S. (2021). PENDINGINAN PANEL SURYA MENGGUNAKAN KOTAK. 9503(2014), 73–79.
El-nagar, D. H., Emam, M., El-betar, A. A., & Nada, S. A. (2024). Performance improvement of building-integrated photovoltaic panels using a composite phase change material-carbon foam heat sink : An experimental study. Journal of Building Engineering, 91(February), 109623. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2024.109623
Hariri, A. Al, Selimli, S., & Dumrul, H. (2022). Effectiveness of heat sink fin position on photovoltaic thermal collector cooling supported by paraffin and steel foam : An experimental study. Applied Thermal Engineering, 213(April), 118784. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2022.118784
Hong, Y., Bai, D., Shi, Y., Zhao, L., Jiao, F., & Du, J. (2024). Experimental study of phase change material heat sinks coupled with Cantor fractal fins for thermal management of photovoltaic systems. Applied Thermal Engineering, 243(January), 122474. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2024.122474
Johnston, E., Szabo, P. S. B., & Bennett, N. S. (2021). Cooling silicon photovoltaic cells using finned heat sinks and the effect of inclination angle. Thermal Science and Engineering Progress, 23(March), 100902. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsep.2021.100902
Krstic, M., Pantic, L., Djordjevic, S., Radonjic, I., Begovic, V., & Radovanovic, B. (2024). Passive cooling of photovoltaic panel by aluminum heat sinks and numerical simulation. Ain Shams Engineering Journal, 15(1), 102330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asej.2023.102330
Lv, S., Duan, J., Lv, G., & Ma, W. (2024). A novel layout of the heat-sink base with a high cooling efficiency for polysilicon reduction furnace. Applied Thermal Engineering, 239(November 2023), 122197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2023.122197
Refaey, H. A., Alharthi, M. A., Bendoukha, S., & Ghani, S. (2023). Case Studies in Thermal Engineering An experimental investigation on passive cooling of a triple-junction solar cell at high concentrations using various straight-finned heat sink configurations. Case Studies in Thermal Engineering, 51(August), 103626. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csite.2023.103626
Sciences, T. (2020). A Numerical Approach to Study the Performance of Photovoltaic Panels by using Aluminium Heat Sink. 2(2), 97–105.
Shahsavar, A., Jha, P., & Baniasad, I. (2022). Experimental study of a nanofluid-based photovoltaic / thermal collector equipped with a grooved helical microchannel heat sink. Applied Thermal Engineering, 217(October 2021), 119281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2022.119281
Singh, S., & Sharma, S. L. (2022). REVIEW PAPER ON THERMAL PERFORMANCE OF HEAT. March. https://doi.org/10.15224/978-1-63248-142-9-34
Sivashankar, M., & Selvam, C. (2022). Experimental investigation on the thermal performance of low-concentrated photovoltaic module using various pin-fin configurations of heat sink with phase change materials. Journal of Energy Storage, 55(PB), 105575. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.est.2022.105575
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
The journal allow the authors to hold the copyright without restrictions and allow the authors to retain publishing rights without restrictions.
Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.
Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See The Effect of Open Access).

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.








