Main Article Content
Abstract
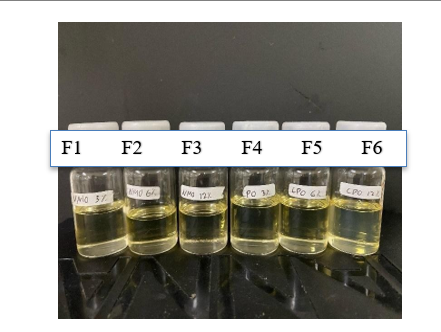
Celecoxib is a selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor widely used for inflammatory conditions; however, its oral administration is associated with gastrointestinal adverse effects, particularly during long-term therapy. Topical delivery using nanoemulsion systems represents a promising alternative to enhance dermal penetration while minimizing systemic side effects. The selection of carrier oil plays a crucial role in determining the physicochemical characteristics, drug release behavior, and skin safety of nanoemulsion formulations.This study aimed to formulate celecoxib nanoemulsions using clove oil and nutmeg oil as carrier oils and to evaluate their physicochemical properties, in vitro drug release profiles, and dermal irritation potential. Celecoxib nanoemulsions were prepared using Tween 80 and polyethylene glycol 400 as surfactant and cosurfactant, with varying concentrations (3%, 6%, and 12%) of clove oil or nutmeg oil. The formulations were evaluated for organoleptic properties, homogeneity, percent transmittance, pH, particle size, and polydispersity index. In vitro drug release was assessed using a Franz diffusion cell with phosphate buffer pH 7.4 as the receptor medium. Dermal irritation was evaluated in New Zealand White rabbits using the primary irritation index method. Results: All nanoemulsion formulations exhibited clear, transparent appearances with nanoscale droplet sizes and acceptable polydispersity indices, indicating uniform particle distribution. The pH values were within the suitable range for topical application. In vitro release studies demonstrated sustained celecoxib release profiles, with no significant differences observed between formulations containing clove oil and nutmeg oil. Dermal irritation testing showed no signs of erythema or edema, resulting in a primary irritation index of zero for all formulations.Celecoxib nanoemulsions formulated with clove oil or nutmeg oil as carrier oils demonstrated favorable physicochemical characteristics, satisfactory drug release behavior, and excellent dermal safety, highlighting their potential as non-irritating topical delivery systems for anti-inflammatory therapy.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
References
- Alhasso, B., & Ghori, M. U. (2022). Systematic Review on the Effectiveness of Essential and Carrier Oils as Skin Penetration Enhancers in Pharmaceutical Formulations.
- BPOM RI. (2022). Peraturan BPOM No 10 Tahun 2022 Pedoman Uji Toksisitas Praklinik Secara In Vivo. BPOM RI, 490, 1–16.
- Deal, B., Reynolds, L. M., Patterson, C., Janjic, J. M., & Pollock, J. A. (2022). Behavioral and inflammatory sex differences revealed by celecoxib nanotherapeutic treatment of peripheral neuroinflammation. Scientific Reports, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-12248-8
- Devi, A. M., Hidayat, A. F., & Priani, S. E. (2020). Formulasi Sediaan Spray Gel Mengandung Nanoemulsi Minyak Cengkeh ( Syzigium Aromaticum L .) untuk Kandidiasis Oral. 567–574.
- Goldenberg, M. M. (1999). Celecoxib, a selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Clinical Therapeutics, 21(9), 1497–1498. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0149-2918(00)80005-3
- Guntama, D., Firmansyah, R. J., & Syfa, T. A. (2021). Analisis Sifat dan Efektivitas Anti-Mikroba Minyak Atsiri Biji Pala ( Myristica Fragrans ) untuk Pemurnian Kualitas Udara pada Ruangan ISO Class 8. 5(1), 45–59.
- Handa, M., Ujjwal, R. R., Vasdev, N., Flora, S. J. S., & Shukla, R. (2021). Optimization of Surfactant- And Cosurfactant-Aided Pine Oil Nanoemulsions by Isothermal Low-Energy Methods for Anticholinesterase Activity. ACS Omega, 6(1), 559–568. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.0c05033
- Kumar, P. S., Febriyanti, R. M., Sofyan, F. F., Luftimas, D. E., & Abdulah, R. (2014). Anticancer potential of Syzygium aromaticum L. in MCF-7 human breast cancer cell lines. Pharmacognosy Research, 6(4), 350–354. https://doi.org/10.4103/0974-8490.138291
- Kurniasari. (2016). Evaluasi Uji Hedonik dan Uji Iritasi Sediaan Lotion Minyak Atsiri Daun Cengkeh ( Eugenia Aromatic L .) Evaluation of Hedonic Test and Irritation Test of Lotion of Clove Leaf Essential Oil ( Eugenia Aromatic L .). Jurnal Farmasi Indonesia, 13(2), 163–170.
- Kurniasari, F., & Widyasti, J. H. (2020). Uji Iritasi dan Uji Sifat Fisik Sediaan Gel Minyak Atsiri Daun Cengkeh ( Syzygium aromaticum ( L .) Merr . & L . M . Perry ) dengan Variasi Konsentrasi HPMC Skin-irritating Test and Physical Properties of Gel Containing Essential Oil of Clove ( Syzygium aromaticum ( L .) Merr . & L . M . Perry ) Leaves with Varied Concentrations of HPMC. 17(01), 187–196.
- Majeed, H. (2025). Development and evaluation of clove oil nanoemulsion-based topical cream for anti-inflammatory activity in mice. December, 1–18. https://doi.org/10.3389/fvets.2025.1716637
- Prabandari, R., & Silvia, A. (2018). ( SYZIGIUM AROMATICUM ) DALAM BASIS LARUT AIR Studi S1 Farmasi Sekolah Tinggi Ilmu eksperimental. 31–39.
- Rachman, E. S., Widji Soeratri, & Tristiana Erawati M. (2023). Characteristics and Physical Stability of Nanoemulsion as a Vehicle for Anti-Aging Cosmetics: A Systematic Review. Jurnal Farmasi Dan Ilmu Kefarmasian Indonesia, 10(1), 62–85. https://doi.org/10.20473/jfiki.v10i12023.62-85
- Sambhakar, S., Malik, R., Bhatia, S., Harrasi, A. Al, Rani, C., Saharan, R., Kumar, S., & Sehrawat, R. (2023). Nanoemulsion : An Emerging Novel Technology for Improving the Bioavailability of Drugs. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1155/2023/6640103
- Shabrina, A., & Khansa, I. S. M. (2022). Physical Stability of Sea Buckthorn Oil Nanoemulsion with Tween 80 Variations Stabilitas Fisik Nanoemulsi Minyak Sea Buckthorn dengan Variasi Tween 80 sebagai Surfaktan. Indonesian Journal of Pharmaceutical Science and Technology Journal Homepage, 1(1), 14–21.
- Shabrina, A., Kumalasari, D., Ramadhani, A., & Sakyajozan, N. (2025). Optimization of Celecoxib Nano-Gel using Nutmeg Oil as A Carrier and Carbopol 940 as A Gel Base with Central Composite Design Method. Pharmaceutical Sciences Asia, 4(Accepted Manuscript), 2025.
- Shabrina, A., Rochman, M. F., Wibowo, D. N., Heroweti, J., Ramadhani, A., Rizkynadia, N. S., Windriyati, Y. N., Sofian, Z. M., & Mahmood, S. (2025). Optimization of celecoxib nanoemulsion formulated using nutmeg oil as a carrier oil by central composite design: In-vitro and in-vivo evaluation. Pharmaceutical Sciences Asia, 52(3), 349–361. https://doi.org/10.29090/psa.2025.03.25.2925
- Shakeel, F., Baboota, S., Ahuja, A., Ali, J., Faisal, M., & Shafiq, S. (2008). Stability evaluation of celecoxib nanoemulsion containing Tween 80. In Thai J. Pharm. Sci (Vol. 32).
- Souto, E. B., Cano, A., Martins-Gomes, C., Coutinho, T. E., Zielińska, A., & Silva, A. M. (2022). Microemulsions and Nanoemulsions in Skin Drug Delivery. Bioengineering, 9(4), 1–22. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9040158
- Srivastava, H., Vishwakarma, A., Kumar, R., & Yadaf, S. (2024). A Review on Nano-Emulgel as a Novel Carrier for Topical Drug Delivery System. Int J PHarm Sci Rev, 84(09), 62–69. https://doi.org/10.47583/ijpsrr.2024.v84i02.009
- Sweetman. (2009). Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference, (36 ed.). Pharmaceutical Press.
- Ticoalu, P. K., Siampa, J. P., & Jayanti, M. (2024). FORMULASI DAN EVALUASI SEDIAAN ROLL ON AROMATERAPI MINYAK CENGKEH ( SYZIGIUM AROMATICUM ) KHAS SULAWESI. 5(September), 9126–9137.
- Waranugraha, Y., Suryana, B. P., & Pratomo, B. (2013). Hubungan Pola Penggunaan OAINS dengan Gejala Klinis Gastropati pada Pasien Reumatik. Jurnal Kedokteran Brawijaya, 26(2), 107–112. https://doi.org/10.21776/ub.jkb.2010.026.02.8
- Widiyastuti, L., & Ikhsanudin, A. (2022.). Aktivitas Repelan Minyak Atsiri Biji Pala ( Myristica Fragrans Houtt .) Pada Nyamuk Aedes Aegypti Repellent Activity Of Nutmeg Essential Oil ( Myristica fragrans Houtt .) on Aedes aegypti. 14–22.
- Widyastuti, A. I., & Saryanti, D. (2023). Jurnal Sains dan Kesehatan (J. Sains Kes.). Jurnal Sains Dan Kesehatan (J. Sains Kes.), 5(2), 178–185.
- Zahro, S. F., Dewi, S. P., Adlia, A., & Rachmawati, H. (2024). Pengembangan formula nanoemulsi minyak cengkeh ( Syzygium aromaticum L .) dan ekstrak siwak ( Salvadora persica ) serta uji aktivitasnya terhadap bakteri dari saliva mencit galur BALB / C. 37(1), 27–43.
References
Alhasso, B., & Ghori, M. U. (2022). Systematic Review on the Effectiveness of Essential and Carrier Oils as Skin Penetration Enhancers in Pharmaceutical Formulations.
BPOM RI. (2022). Peraturan BPOM No 10 Tahun 2022 Pedoman Uji Toksisitas Praklinik Secara In Vivo. BPOM RI, 490, 1–16.
Deal, B., Reynolds, L. M., Patterson, C., Janjic, J. M., & Pollock, J. A. (2022). Behavioral and inflammatory sex differences revealed by celecoxib nanotherapeutic treatment of peripheral neuroinflammation. Scientific Reports, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-12248-8
Devi, A. M., Hidayat, A. F., & Priani, S. E. (2020). Formulasi Sediaan Spray Gel Mengandung Nanoemulsi Minyak Cengkeh ( Syzigium Aromaticum L .) untuk Kandidiasis Oral. 567–574.
Goldenberg, M. M. (1999). Celecoxib, a selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Clinical Therapeutics, 21(9), 1497–1498. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0149-2918(00)80005-3
Guntama, D., Firmansyah, R. J., & Syfa, T. A. (2021). Analisis Sifat dan Efektivitas Anti-Mikroba Minyak Atsiri Biji Pala ( Myristica Fragrans ) untuk Pemurnian Kualitas Udara pada Ruangan ISO Class 8. 5(1), 45–59.
Handa, M., Ujjwal, R. R., Vasdev, N., Flora, S. J. S., & Shukla, R. (2021). Optimization of Surfactant- And Cosurfactant-Aided Pine Oil Nanoemulsions by Isothermal Low-Energy Methods for Anticholinesterase Activity. ACS Omega, 6(1), 559–568. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.0c05033
Kumar, P. S., Febriyanti, R. M., Sofyan, F. F., Luftimas, D. E., & Abdulah, R. (2014). Anticancer potential of Syzygium aromaticum L. in MCF-7 human breast cancer cell lines. Pharmacognosy Research, 6(4), 350–354. https://doi.org/10.4103/0974-8490.138291
Kurniasari. (2016). Evaluasi Uji Hedonik dan Uji Iritasi Sediaan Lotion Minyak Atsiri Daun Cengkeh ( Eugenia Aromatic L .) Evaluation of Hedonic Test and Irritation Test of Lotion of Clove Leaf Essential Oil ( Eugenia Aromatic L .). Jurnal Farmasi Indonesia, 13(2), 163–170.
Kurniasari, F., & Widyasti, J. H. (2020). Uji Iritasi dan Uji Sifat Fisik Sediaan Gel Minyak Atsiri Daun Cengkeh ( Syzygium aromaticum ( L .) Merr . & L . M . Perry ) dengan Variasi Konsentrasi HPMC Skin-irritating Test and Physical Properties of Gel Containing Essential Oil of Clove ( Syzygium aromaticum ( L .) Merr . & L . M . Perry ) Leaves with Varied Concentrations of HPMC. 17(01), 187–196.
Majeed, H. (2025). Development and evaluation of clove oil nanoemulsion-based topical cream for anti-inflammatory activity in mice. December, 1–18. https://doi.org/10.3389/fvets.2025.1716637
Prabandari, R., & Silvia, A. (2018). ( SYZIGIUM AROMATICUM ) DALAM BASIS LARUT AIR Studi S1 Farmasi Sekolah Tinggi Ilmu eksperimental. 31–39.
Rachman, E. S., Widji Soeratri, & Tristiana Erawati M. (2023). Characteristics and Physical Stability of Nanoemulsion as a Vehicle for Anti-Aging Cosmetics: A Systematic Review. Jurnal Farmasi Dan Ilmu Kefarmasian Indonesia, 10(1), 62–85. https://doi.org/10.20473/jfiki.v10i12023.62-85
Sambhakar, S., Malik, R., Bhatia, S., Harrasi, A. Al, Rani, C., Saharan, R., Kumar, S., & Sehrawat, R. (2023). Nanoemulsion : An Emerging Novel Technology for Improving the Bioavailability of Drugs. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1155/2023/6640103
Shabrina, A., & Khansa, I. S. M. (2022). Physical Stability of Sea Buckthorn Oil Nanoemulsion with Tween 80 Variations Stabilitas Fisik Nanoemulsi Minyak Sea Buckthorn dengan Variasi Tween 80 sebagai Surfaktan. Indonesian Journal of Pharmaceutical Science and Technology Journal Homepage, 1(1), 14–21.
Shabrina, A., Kumalasari, D., Ramadhani, A., & Sakyajozan, N. (2025). Optimization of Celecoxib Nano-Gel using Nutmeg Oil as A Carrier and Carbopol 940 as A Gel Base with Central Composite Design Method. Pharmaceutical Sciences Asia, 4(Accepted Manuscript), 2025.
Shabrina, A., Rochman, M. F., Wibowo, D. N., Heroweti, J., Ramadhani, A., Rizkynadia, N. S., Windriyati, Y. N., Sofian, Z. M., & Mahmood, S. (2025). Optimization of celecoxib nanoemulsion formulated using nutmeg oil as a carrier oil by central composite design: In-vitro and in-vivo evaluation. Pharmaceutical Sciences Asia, 52(3), 349–361. https://doi.org/10.29090/psa.2025.03.25.2925
Shakeel, F., Baboota, S., Ahuja, A., Ali, J., Faisal, M., & Shafiq, S. (2008). Stability evaluation of celecoxib nanoemulsion containing Tween 80. In Thai J. Pharm. Sci (Vol. 32).
Souto, E. B., Cano, A., Martins-Gomes, C., Coutinho, T. E., Zielińska, A., & Silva, A. M. (2022). Microemulsions and Nanoemulsions in Skin Drug Delivery. Bioengineering, 9(4), 1–22. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9040158
Srivastava, H., Vishwakarma, A., Kumar, R., & Yadaf, S. (2024). A Review on Nano-Emulgel as a Novel Carrier for Topical Drug Delivery System. Int J PHarm Sci Rev, 84(09), 62–69. https://doi.org/10.47583/ijpsrr.2024.v84i02.009
Sweetman. (2009). Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference, (36 ed.). Pharmaceutical Press.
Ticoalu, P. K., Siampa, J. P., & Jayanti, M. (2024). FORMULASI DAN EVALUASI SEDIAAN ROLL ON AROMATERAPI MINYAK CENGKEH ( SYZIGIUM AROMATICUM ) KHAS SULAWESI. 5(September), 9126–9137.
Waranugraha, Y., Suryana, B. P., & Pratomo, B. (2013). Hubungan Pola Penggunaan OAINS dengan Gejala Klinis Gastropati pada Pasien Reumatik. Jurnal Kedokteran Brawijaya, 26(2), 107–112. https://doi.org/10.21776/ub.jkb.2010.026.02.8
Widiyastuti, L., & Ikhsanudin, A. (2022.). Aktivitas Repelan Minyak Atsiri Biji Pala ( Myristica Fragrans Houtt .) Pada Nyamuk Aedes Aegypti Repellent Activity Of Nutmeg Essential Oil ( Myristica fragrans Houtt .) on Aedes aegypti. 14–22.
Widyastuti, A. I., & Saryanti, D. (2023). Jurnal Sains dan Kesehatan (J. Sains Kes.). Jurnal Sains Dan Kesehatan (J. Sains Kes.), 5(2), 178–185.
Zahro, S. F., Dewi, S. P., Adlia, A., & Rachmawati, H. (2024). Pengembangan formula nanoemulsi minyak cengkeh ( Syzygium aromaticum L .) dan ekstrak siwak ( Salvadora persica ) serta uji aktivitasnya terhadap bakteri dari saliva mencit galur BALB / C. 37(1), 27–43.