Main Article Content
Abstract
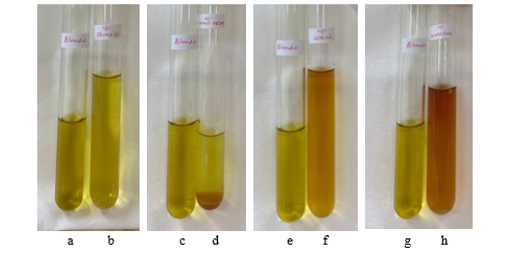
Jamu X, which is available in the market, has a simple composition consisting of noni fruit (Morinda citrifolia L.), celery herb (Apium graveolens L.), cat's whiskers leaves (Orthosiphon aristatus), pule bark (Alstoniae scholaris), meniran herb (Phyllanthus niruri), gotu kola herb (Centella asiatica), sembung leaves (Blumea balsamifera), plantain leaves (Plantago major), and andrographis herb (Andrographis paniculata). Jamu X is claimed to help lower blood pressure. All plants in jamu X contain flavonoids. This study aims to confirm the presence of flavonoids and prove the antihypertensive effect of jamu X on rats induced with monosodium glutamate (MSG). The presence of flavonoids was determined through test tube and thin-layer chromatography (TLC) tests. The research method employed is a randomised controlled group pretest and posttest design. Hypertensive mice were induced by administering MSG 100 mg/kg body weight/day orally for 14 days. The hypertensive rats were divided into five treatment groups: Group I rats (negative control) received CMC Na 0.5% 12.5 mL/kg body weight. Group II rats (positive control) received captopril at a dose of 2.5 mg/kg body weight/day. Group III, IV, and V rats were given jamu X at doses of 0.09, 0.18 capsules/kg body weight, once a day, and 0.18 capsules/kg body weight, twice a day, respectively. The test substance was administered orally for 14 days. The significance of the difference between systolic and diastolic blood pressure was tested using a paired t-test at a 95% confidence level. Jamu X was declared to have antihypertensive activity if there was a decrease and a significant difference in systolic and diastolic blood pressure before and after the administration of jamu X. Flavonoids were declared to be contained in jamu X. Based on the tests performed, jamu X showed antihypertensive activity at all doses.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.