Main Article Content
Abstract
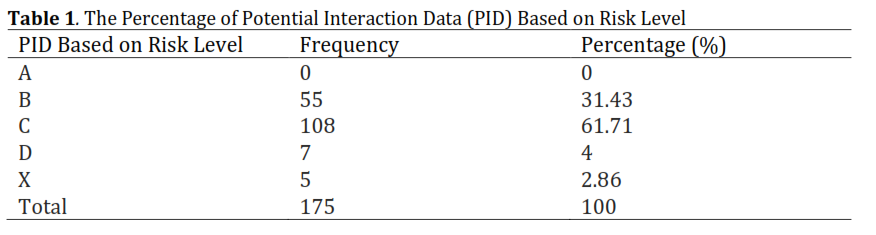
One of the factors that cause chronic kidney disease is comorbid diseases. Comorbidities can lead to polypharmacy, which can increase the potential for drug interactions. Potential drug interactions, if not addressed, can increase the incidence of morbidity and mortality. The purpose of the study was to identify potential drug interactions with drugs for patients with chronic kidney disease using the Lexicomp® application in terms of risk level, severity, and recommendations for the treatment of drug interactions. The study was conducted at Ansari Saleh Hospital, Banjarmasin, from January to February 2024. The study sample consisted of 58 patients. Data were analyzed using the Lexicomp® application. The results showed that 56.90% of the patients had potential drug interactions, with 175 cases of potential drug interactions in 53 drug combinations. The percentage of potential drug interactions based on risk level was 31.43% (category B), 61.71% (category C), 4% (category D), and 2.86% (category X). The percentage of potential drug interactions according to severity was 33.71% (minor), 62.29% (moderate), and 4% (major). Treatment recommendations for drug interactions with drugs include not need for action, monitoring therapy, and dose adjustment. Potential drug interactions with drugs for patients with chronic kidney disease using the Lexicomp® application in terms of the majority of risk levels in category C, the severity of most moderate categories, and recommendations for handling drug interactions for the majority need to monitor therapy and dose adjustments. Chronic kidney disease patients have the potential to experience moderate drug-drug interactions of the category, with treatment recommendations that require therapeutic monitoring.
Keywords
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
References
- Agustin, OA & Fitrianingsih, F. 2020. Kajian Interaksi Obat Berdasarkan Kategori Signifikansi Klinis Terhadap Pola Peresepan Pasien Rawat Jalan Di Apotek X Jambi. Electronic Journal Scientific of Environmental Health And Disease. 1(1). doi.org/10.22437/esehad.v1i1.10759.
- Ginting, W. 2018. Sistem Pakar Mendiagnosa Penyakit Ginjal Menggunakan Metode Case Based Reasoning. Information System Development (ISD). 3(2):120–125.
- Hakim, L & Arfania, M. 2022. Interaksi Obat Mekanisme Dan Implikasi Klinik. Jakarta: Adipura Book Centre.
- Hammoud, KM, Sridhar, SB, Rabbani, SA & Kurian, MT. 2022. Evaluation of potential drug-drug interactions and adverse drug reactions among chronic kidney disease patients: An experience from United Arab Emirates. Tropical Journal of Pharmaceutical Research. 21(4):853–861. doi.org/10.4314/tjpr.v21i4.24.
- Handayani, N, Faisal, M & Rusli, R. 2023. Kajian Interaksi Obat pada Pasien Gagal Ginjal Rawat Inap di RSUD Panglima Sebaya Tanah Grogot: Drug Interaction Studies in Patients with Kidney Failure Inpatient at Panglima Sebaya Hospital, Tanah Grogot. Jurnal Sains dan Kesehatan. 5:500–506. doi.org/10.25026/jsk.v5i4.1168.
- Hutagaol, EF. 2017. Peningkatan Kualitas Hidup Pada Penderita Gagal Ginjal Kronik Yang Menjalani Terapi Hemodialisa Melalui Psychological Intervention Di Unit Hemodialisa RS Royal Prima Medan Tahun 2016. JUMANTIK (Jurnal Ilmiah Penelitian Kesehatan). 2(1):42–59. doi.org/10.30829/jumantik.v2i1.968.
- ISN. 2023. Global Kidney Health Atlas. Available from: https://www.theisn.org/initiatives/global-kidney-health-atlas/ [Accessed 30 July 2024].
- Kemenkes, R. 2018. Laporan Nasional Riskesdas Tahun 2018. Jakarta: Kementerian Kesehatan Republik Indonesia.
- Lexicomp. 2024. Available from: https://www.wolterskluwer.com/en/solutions/lexicomp/lexicomp.
- Lule, AP, Delic, OB, Katunguka, K, Muwonge, F & Yadesa, TM. 2024. Prevalence and factors associated with potential drug-drug interactions in prescriptions presented at private pharmacies in Mbarara city, southwestern Uganda. BMC Pharmacology and Toxicology. 25(1):2. doi.org/10.1186/s40360-023-00719-1.
- Maifitrianti, M. 2016. Identifying Potential Drug-Drug Interactions Among Chronic Kidney Disease. Farmasains : Jurnal Ilmiah Ilmu Kefarmasian. 3(2):59–63. doi.org/10.22236/farmasains.v3i2.3322.
References
Agustin, OA & Fitrianingsih, F. 2020. Kajian Interaksi Obat Berdasarkan Kategori Signifikansi Klinis Terhadap Pola Peresepan Pasien Rawat Jalan Di Apotek X Jambi. Electronic Journal Scientific of Environmental Health And Disease. 1(1). doi.org/10.22437/esehad.v1i1.10759.
Ginting, W. 2018. Sistem Pakar Mendiagnosa Penyakit Ginjal Menggunakan Metode Case Based Reasoning. Information System Development (ISD). 3(2):120–125.
Hakim, L & Arfania, M. 2022. Interaksi Obat Mekanisme Dan Implikasi Klinik. Jakarta: Adipura Book Centre.
Hammoud, KM, Sridhar, SB, Rabbani, SA & Kurian, MT. 2022. Evaluation of potential drug-drug interactions and adverse drug reactions among chronic kidney disease patients: An experience from United Arab Emirates. Tropical Journal of Pharmaceutical Research. 21(4):853–861. doi.org/10.4314/tjpr.v21i4.24.
Handayani, N, Faisal, M & Rusli, R. 2023. Kajian Interaksi Obat pada Pasien Gagal Ginjal Rawat Inap di RSUD Panglima Sebaya Tanah Grogot: Drug Interaction Studies in Patients with Kidney Failure Inpatient at Panglima Sebaya Hospital, Tanah Grogot. Jurnal Sains dan Kesehatan. 5:500–506. doi.org/10.25026/jsk.v5i4.1168.
Hutagaol, EF. 2017. Peningkatan Kualitas Hidup Pada Penderita Gagal Ginjal Kronik Yang Menjalani Terapi Hemodialisa Melalui Psychological Intervention Di Unit Hemodialisa RS Royal Prima Medan Tahun 2016. JUMANTIK (Jurnal Ilmiah Penelitian Kesehatan). 2(1):42–59. doi.org/10.30829/jumantik.v2i1.968.
ISN. 2023. Global Kidney Health Atlas. Available from: https://www.theisn.org/initiatives/global-kidney-health-atlas/ [Accessed 30 July 2024].
Kemenkes, R. 2018. Laporan Nasional Riskesdas Tahun 2018. Jakarta: Kementerian Kesehatan Republik Indonesia.
Lexicomp. 2024. Available from: https://www.wolterskluwer.com/en/solutions/lexicomp/lexicomp.
Lule, AP, Delic, OB, Katunguka, K, Muwonge, F & Yadesa, TM. 2024. Prevalence and factors associated with potential drug-drug interactions in prescriptions presented at private pharmacies in Mbarara city, southwestern Uganda. BMC Pharmacology and Toxicology. 25(1):2. doi.org/10.1186/s40360-023-00719-1.
Maifitrianti, M. 2016. Identifying Potential Drug-Drug Interactions Among Chronic Kidney Disease. Farmasains : Jurnal Ilmiah Ilmu Kefarmasian. 3(2):59–63. doi.org/10.22236/farmasains.v3i2.3322.