Main Article Content
Abstract
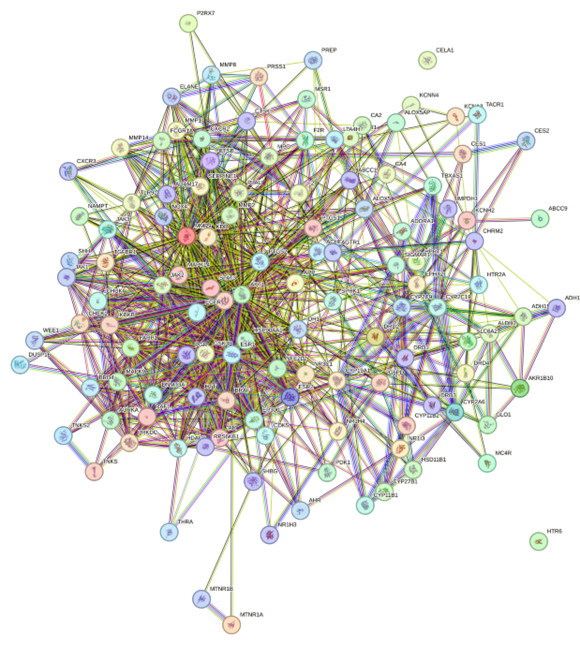
Diabetes mellitus is a non-communicable disease with a high prevalence that has the potential to cause chronic complications, such as diabetic nephropathy (ND). Diabetic nephropathy is characterized by microalbuminuria, decreased glomerular filtration rate, and the risk of end-stage renal failure. Conventional treatment with oral hypoglycemic drugs often causes side effects such as hyperkalemia and impaired heart function. This indicates the need for alternative therapies with high effectiveness, low toxicity, and affordable costs. This study explores the potential of black turmeric as a therapeutic agent for diabetic nephropathy through an in-silico approach. The active compounds of black turmeric were analyzed for their pharmacokinetics using SwissADME based on Lipinski's rules. The target proteins of the compounds were obtained through SwissTargetPrediction and compared with ND-encoding proteins from GeneCards using Venny 2.1. Specific proteins were analyzed for protein-protein interactions through STRING and visualized with pharmacological networks using Cytoscape. In-depth analysis was carried out to identify biological pathways through KEGG and molecular activity using WebGestalt. The results showed that black turmeric has 123 specific target proteins for ND, with EGFR and STAT3 as core proteins that play a role in regulating apoptosis, inflammation, and insulin sensitivity. Curcumin showed significant activity on the AGE-RAGE and FoxO pathways, which are relevant for the treatment of ND. This study provides initial insight into the potential of black turmeric as an alternative therapy for diabetic nephropathy
Keywords
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
References
- Abdul-Hammed, M. et al. (2022) ‘Virtual screening, ADMET profiling, PASS prediction, and bioactivity studies of potential inhibitory roles of alkaloids, phytosterols, and flavonoids against COVID-19 main protease (Mpro)’, Natural Product Research, 36(12), pp. 3110–3116. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2021.1935933.
- Abdullah, S.S. et al. (2021) ‘ANALISIS SIFAT FISIKOKIMIA, FARMAKOKINETIK DAN TOKSIKOLOGI PADA PERICARPIUM PALA (Myristica fragransa) SECARA ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE’, CHEMISTRY PROGRESS, 14(2), p. 81. Available at: https://doi.org/10.35799/cp.14.2.2021.37112.
- ADA (2022) ‘2 . Klasifikasi dan Diagnosis Diabetes : Standar dari peduli Diabetes — 2022 Medis’, 45, pp. 17–38.
- Aldukhayel, A. (2017) ‘Prevalence of diabetic nephropathy among type 2 diabetic patients in some of the arab countries’, International Journal of Health Science, 11(1), pp. 60–63.
- Aleksander, S.A. et al. (2023) ‘The Gene Ontology knowledgebase in 2023’, Genetics, 224(1). Available at: https://doi.org/10.1093/genetics/iyad031.
- Baghel, S.S. et al. (2013) ‘Pharmacological activities of Curcuma caesia’, International Journal of Green Pharmacy, 7(1), pp. 1–5. Available at: https://doi.org/10.4103/0973-8258.111590.
- Bhupendra Sahu, Rameshroo Kenwat and Shashikant Chandrakar (2016) ‘Medicinal Value of Curcuma cassia roxb: An Overview’, Pharmaceutical and Biosciences Journal, pp. 69–74. Available at: https://doi.org/10.20510/ukjpb/4/i6/134671.
- Chen, J., Chen, J.K. and Harris, R.C. (2015) ‘EGF receptor deletion in podocytes attenuates diabetic nephropathy’, Journal of the American Society of Nephrology, 26(5), pp. 1115–1125. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2014020192.
- Flores-HolguÃn, N., Frau, J. and Glossman-Mitnik, D. (2021) ‘Computational Pharmacokinetics Report, ADMET Study and Conceptual DFT-Based Estimation of the Chemical Reactivity Properties of Marine Cyclopeptides’, ChemistryOpen, 10(11), pp. 1142–1149. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1002/open.202100178.
- Hou, Z. et al. (2021) ‘PIAS1 alleviates diabetic peripheral neuropathy through SUMOlation of PPAR-γ and miR-124-induced downregulation of EZH2/STAT3’, Cell Death Discovery, 7(1). Available at: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41420-021-00765-w.
- Hu, F. et al. (2024) ‘Exploring the molecular mechanism of Xuebifang in the treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathy based on bioinformatics and network pharmacology’, Frontiers in Endocrinology, 15. Available at: https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2024.1275816.
- Kanehisa, M. (2019) ‘Toward understanding the origin and evolution of cellular organisms’, Protein Science. Blackwell Publishing Ltd, pp. 1947–1951. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1002/pro.3715.
- Kanehisa, M. et al. (2023) ‘KEGG for taxonomy-based analysis of pathways and genomes’, Nucleic Acids Research, 51(D1), pp. D587–D592. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkac963.
- Kanehisa, M., Sato, Y. and Kawashima, M. (2022) ‘KEGG mapping tools for uncovering hidden features in biological data’, Protein Science, 31(1), pp. 47–53. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1002/pro.4172.
- Kemenkes RI (2023) ‘Ditjen P2P Laporan Kinerja Semester I Tahun 2023’, kemenkes RI, pp. 1–134.
- Kim, T.H. et al. (2023) ‘Network Pharmacological Analysis of a New Herbal Combination Targeting Hyperlipidemia and Efficacy Validation In Vitro’, Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 45(2), pp. 1314–1332. Available at: https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb45020086.
- Li, Z. et al. (2018) ‘Inhibition of epidermal growth factor receptor activation is associated with improved diabetic nephropathy and insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes’, Diabetes, 67(9), pp. 1847–1857. Available at: https://doi.org/10.2337/db17-1513.
- Malik, M. et al. (2021) ‘Acta Pharm Indo’, Acta Pharmaciae Indonesia : Acta Pharm Indo, 9 (1)(1), pp. 70–77. Available at: http://jos.unsoed.ac.id/index.php/api/article/view/3323.
- Moradi, M. et al. (2022) ‘A contemporary review on the important role of in silico approaches for managing different aspects of COVID-19 crisis’, Informatics in Medicine Unlocked. Elsevier Ltd. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imu.2022.100862.
- Oh, K.K., Adnan, M. and Cho, D.H. (2021) ‘Network pharmacology approach to decipher signaling pathways associated with target proteins of NSAIDs against COVID-19’, Scientific Reports, 11(1). Available at: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-88313-5.
- Rochette, S. et al. (2015) ‘Genome-wide protein-protein interaction screening by protein-fragment complementation assay (PCA) in living cells’, Journal of Visualized Experiments, 2015(97). Available at: https://doi.org/10.3791/52255.
- Saik, O. V. and Klimontov, V. V. (2020) ‘Bioinformatic reconstruction and analysis of gene networks related to glucose variability in diabetes and its complications’, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(22), pp. 1–20. Available at: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21228691.
- Sheng, L., Bayliss, G. and Zhuang, S. (2021) ‘Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor: A Potential Therapeutic Target for Diabetic Kidney Disease’, Frontiers in Pharmacology. Frontiers Media S.A. Available at: https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.598910.
- Soleymani, F. et al. (2022) ‘Protein–protein interaction prediction with deep learning: A comprehensive review’, Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal. Elsevier B.V., pp. 5316–5341. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csbj.2022.08.070.
- Thomas, M.C. et al. (2020) ‘HHS Public Access’, pp. 1–46. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1038/nrdp.2015.18.Diabetic.
- Tung, C.W. et al. (2018) ‘Glomerular mesangial cell and podocyte injuries in diabetic nephropathy’, Nephrology. Blackwell Publishing, pp. 32–37. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1111/nep.13451.
References
Abdul-Hammed, M. et al. (2022) ‘Virtual screening, ADMET profiling, PASS prediction, and bioactivity studies of potential inhibitory roles of alkaloids, phytosterols, and flavonoids against COVID-19 main protease (Mpro)’, Natural Product Research, 36(12), pp. 3110–3116. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2021.1935933.
Abdullah, S.S. et al. (2021) ‘ANALISIS SIFAT FISIKOKIMIA, FARMAKOKINETIK DAN TOKSIKOLOGI PADA PERICARPIUM PALA (Myristica fragransa) SECARA ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE’, CHEMISTRY PROGRESS, 14(2), p. 81. Available at: https://doi.org/10.35799/cp.14.2.2021.37112.
ADA (2022) ‘2 . Klasifikasi dan Diagnosis Diabetes : Standar dari peduli Diabetes — 2022 Medis’, 45, pp. 17–38.
Aldukhayel, A. (2017) ‘Prevalence of diabetic nephropathy among type 2 diabetic patients in some of the arab countries’, International Journal of Health Science, 11(1), pp. 60–63.
Aleksander, S.A. et al. (2023) ‘The Gene Ontology knowledgebase in 2023’, Genetics, 224(1). Available at: https://doi.org/10.1093/genetics/iyad031.
Baghel, S.S. et al. (2013) ‘Pharmacological activities of Curcuma caesia’, International Journal of Green Pharmacy, 7(1), pp. 1–5. Available at: https://doi.org/10.4103/0973-8258.111590.
Bhupendra Sahu, Rameshroo Kenwat and Shashikant Chandrakar (2016) ‘Medicinal Value of Curcuma cassia roxb: An Overview’, Pharmaceutical and Biosciences Journal, pp. 69–74. Available at: https://doi.org/10.20510/ukjpb/4/i6/134671.
Chen, J., Chen, J.K. and Harris, R.C. (2015) ‘EGF receptor deletion in podocytes attenuates diabetic nephropathy’, Journal of the American Society of Nephrology, 26(5), pp. 1115–1125. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2014020192.
Flores-HolguÃn, N., Frau, J. and Glossman-Mitnik, D. (2021) ‘Computational Pharmacokinetics Report, ADMET Study and Conceptual DFT-Based Estimation of the Chemical Reactivity Properties of Marine Cyclopeptides’, ChemistryOpen, 10(11), pp. 1142–1149. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1002/open.202100178.
Hou, Z. et al. (2021) ‘PIAS1 alleviates diabetic peripheral neuropathy through SUMOlation of PPAR-γ and miR-124-induced downregulation of EZH2/STAT3’, Cell Death Discovery, 7(1). Available at: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41420-021-00765-w.
Hu, F. et al. (2024) ‘Exploring the molecular mechanism of Xuebifang in the treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathy based on bioinformatics and network pharmacology’, Frontiers in Endocrinology, 15. Available at: https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2024.1275816.
Kanehisa, M. (2019) ‘Toward understanding the origin and evolution of cellular organisms’, Protein Science. Blackwell Publishing Ltd, pp. 1947–1951. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1002/pro.3715.
Kanehisa, M. et al. (2023) ‘KEGG for taxonomy-based analysis of pathways and genomes’, Nucleic Acids Research, 51(D1), pp. D587–D592. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkac963.
Kanehisa, M., Sato, Y. and Kawashima, M. (2022) ‘KEGG mapping tools for uncovering hidden features in biological data’, Protein Science, 31(1), pp. 47–53. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1002/pro.4172.
Kemenkes RI (2023) ‘Ditjen P2P Laporan Kinerja Semester I Tahun 2023’, kemenkes RI, pp. 1–134.
Kim, T.H. et al. (2023) ‘Network Pharmacological Analysis of a New Herbal Combination Targeting Hyperlipidemia and Efficacy Validation In Vitro’, Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 45(2), pp. 1314–1332. Available at: https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb45020086.
Li, Z. et al. (2018) ‘Inhibition of epidermal growth factor receptor activation is associated with improved diabetic nephropathy and insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes’, Diabetes, 67(9), pp. 1847–1857. Available at: https://doi.org/10.2337/db17-1513.
Malik, M. et al. (2021) ‘Acta Pharm Indo’, Acta Pharmaciae Indonesia : Acta Pharm Indo, 9 (1)(1), pp. 70–77. Available at: http://jos.unsoed.ac.id/index.php/api/article/view/3323.
Moradi, M. et al. (2022) ‘A contemporary review on the important role of in silico approaches for managing different aspects of COVID-19 crisis’, Informatics in Medicine Unlocked. Elsevier Ltd. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imu.2022.100862.
Oh, K.K., Adnan, M. and Cho, D.H. (2021) ‘Network pharmacology approach to decipher signaling pathways associated with target proteins of NSAIDs against COVID-19’, Scientific Reports, 11(1). Available at: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-88313-5.
Rochette, S. et al. (2015) ‘Genome-wide protein-protein interaction screening by protein-fragment complementation assay (PCA) in living cells’, Journal of Visualized Experiments, 2015(97). Available at: https://doi.org/10.3791/52255.
Saik, O. V. and Klimontov, V. V. (2020) ‘Bioinformatic reconstruction and analysis of gene networks related to glucose variability in diabetes and its complications’, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(22), pp. 1–20. Available at: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21228691.
Sheng, L., Bayliss, G. and Zhuang, S. (2021) ‘Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor: A Potential Therapeutic Target for Diabetic Kidney Disease’, Frontiers in Pharmacology. Frontiers Media S.A. Available at: https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.598910.
Soleymani, F. et al. (2022) ‘Protein–protein interaction prediction with deep learning: A comprehensive review’, Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal. Elsevier B.V., pp. 5316–5341. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csbj.2022.08.070.
Thomas, M.C. et al. (2020) ‘HHS Public Access’, pp. 1–46. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1038/nrdp.2015.18.Diabetic.
Tung, C.W. et al. (2018) ‘Glomerular mesangial cell and podocyte injuries in diabetic nephropathy’, Nephrology. Blackwell Publishing, pp. 32–37. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1111/nep.13451.